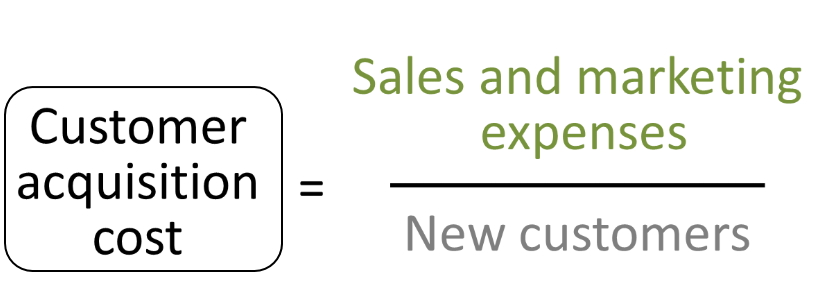
Understanding your Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) is a key retail element today. We use it in marketing budgeting. I will show you how to calculate it to ensure your marketing budget delivers accurate results.
What is Customer Acquisition Cost(CAC)?
Customer acquisition cost, or CAC, is the cost of acquiring a new customer. Different channels, like social media, newspapers, email newsletters, etc., have different costs and effectiveness. We are trying to determine the most successful channel for the cost vs new customers.
To calculate your CAC, we divide your total marketing costs, including advertising costs, promotions, event expenses, product giveaways, and even extra salaries related to marketing efforts, by the number of new customers you gain.
Why CAC Matters
Knowing your CAC helps you:
- Evaluate the effectiveness of different marketing channels
- Allowing you to allocate your marketing budget more efficiently
- Understand the actual cost of growing your customer base
- Make data-driven decisions about your marketing strategies
Calculating CAC with Your POS System
Your point-of-sale system is crucial for accurate CAC calculations. Here's how to use it:
- Compare current sales to the same period last year
- Adjust for overall business growth or decline
- Identify the number of new customers gained by a recent advertisement.
For example, suppose you averaged 100 sales per day last year and made 105 sales per day this year during a promotion. In that case, we had 5 new sales. This year's business is up about 2% compared to last year's figures, so we have five new sales, less than the two we would have had anyway. So, we are looking at three new sales per day due to this advertisement.
Real-World Examples
Let's crunch some numbers to see CAC in action:
Newspaper Advertisement
- Cost: $200 (design) + $1,000 (placement) = $1,200
- New customers: 10
- CAC = $1,200 / 10 = $120 per customer
Facebook Advertisement
- Cost: $200
- New customers: 1
- CAC = $200 / 1 = $200 per customer
Google Marketing Campaign
- Cost: $600
- New customers: 5
- CAC = $600 / 5 = $120 per customer
In-Store Sign
- Cost: $300
- New customers: 6
- CAC = $300 / 6 = $50 per customer
In this scenario, the in-store sign proves most cost-effective.
Beyond the Basics
Customer Value Assessment
Some people prefer profit over sales because a high-margin giftware buyer is worth more than a newspaper purchaser. I support this view. One of the problems here often is that something is popular; prices are thin, and you promote it, which gets some customers but little profit. The cost of the advertisement is actual.
Your POS System can give you the profit figures.
Fixed Cost Considerations
Sometimes, CAC calculations include fixed costs. The new shop should give you four new customers for two shop locations with a difference of $200 extra monthly rent. To a marketer, the CAC = $200 / 4 = $50 per monthly customer. Is $50 a customer worth it to you as a business owner?
Implementation Steps
- Get figures before the promotion of what your current customers are.
- Experiment with different marketing strategies and track results
- Calculate the CAC results; the more you do, the easier it gets.
- Regularly review and adjust your marketing mix based on CAC data
By mastering your Customer Acquisition Cost, you'll make smarter marketing decisions, stretch your budget further, and build a loyal customer base that will support your business for years. Keep experimenting, tracking, and refining your approach—your bottom line will thank you!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Why should I use CAC in my business?
A: CAC should be used in your business as it helps optimise your marketing and sales budget allocation by showing exactly how much you're spending to gain each new customer, allowing you to identify inefficiencies and reduce wasteful spending.
Q: How is CAC calculated?
A: Divide the total cost of sales and marketing by the number of new customers acquired during a specific period.
The formula is: CAC = (Cost of Sales and Marketing) / (Number of New Customers)
The costs include all costs associated with acquiring customers, such as salaries, tools, advertising expenses, and related overhead.
Q: What is a reasonable CAC?
A: The cost of a CAC varies significantly by industry. In Australia, retail prices are generally about $60. If you are starting a business, it's often higher.


